
Introdução
No ambiente empresarial atual, garantir a conformidade com políticas de segurança é crucial. Automatizar esse processo pode simplificar significativamente a gestão de conformidade. Neste artigo, exploraremos como implementar uma função do Azure para criar e atribuir políticas de conformidade de forma automatizada, utilizando TypeScript e Microsoft Graph API e baseado no conteúdo do Marcelo do Cloud na Quebrada, posso dizer que gerenciar políticas de conformidade nunca foi tão fácil com automação e Azure Functions.
Configuração do Ambiente
Antes de começarmos, é necessário configurar algumas variáveis de ambiente no Azure Portal:
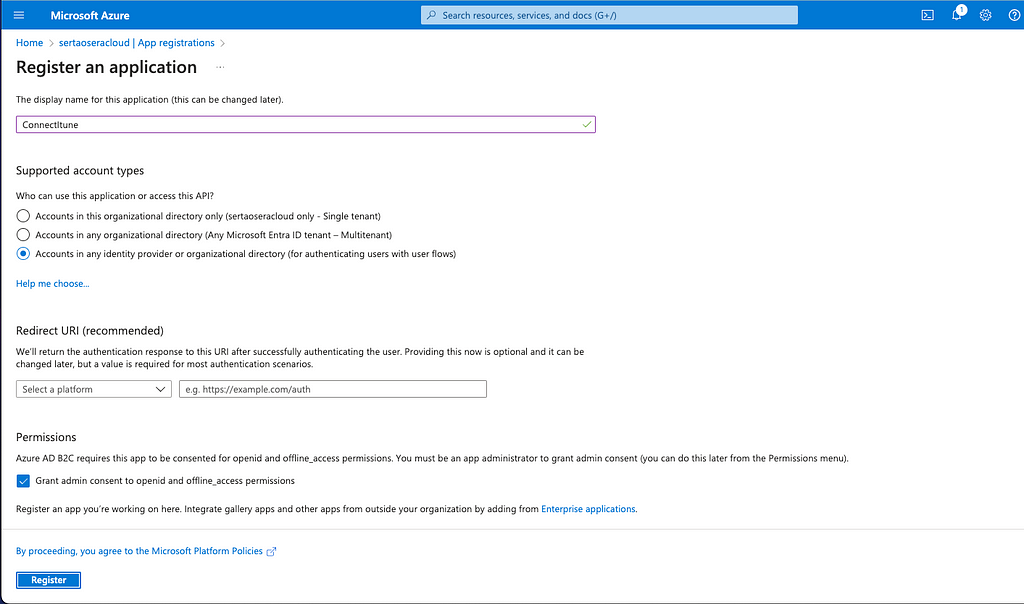
- CLIENT_ID: ID do cliente Azure AD para autenticação.
- CLIENT_SECRET: Segredo do cliente Azure AD.
- TENANT_ID: ID do locatário Azure AD.
Implementação da Função Azure
import { AzureFunction, Context, HttpRequest } from "@azure/functions";
import { ServicePrincipal } from "../src/service/ServicePrincipal";
import { CompliancePolicies } from "../src/service/CompliancePolicies";
/**
* HTTP trigger function for processing compliance policy assignments.
*
* @param {Context} context - The context object for the Azure Function.
* @param {HttpRequest} req - The HTTP request object.
* @returns {Promise<void>} - A promise that resolves when the function completes.
*/
const httpTrigger: AzureFunction = async function (context: Context, req: HttpRequest): Promise<void> {
try {
context.log('HTTP trigger function processed a request.');
// Validate request method
if (req.method !== "POST") {
context.res = {
status: 405,
body: "Method Not Allowed",
};
return;
}
// Extract environment variables
const clientId: string = String(process.env.CLIENT_ID);
const clientSecret: string = String(process.env.CLIENT_SECRET);
const tenantId: string = String(process.env.TENANT_ID);
// Initialize ServicePrincipal with Azure AD credentials
context.log('Initializing ServicePrincipal with tenantId:', tenantId);
const servicePrincipal = new ServicePrincipal(tenantId, clientId, clientSecret);
// Request access token from Azure AD
context.log('Requesting access token');
const accessToken: string = await servicePrincipal.getAccessToken();
context.log('Access token received');
// Initialize CompliancePolicies instance with request parameters
const compliancePolicies = new CompliancePolicies(req.body.name, req.body.description);
context.log('Initialized CompliancePolicies with name:', req.body.name, 'and description:', req.body.description);
// Check if complianceid is provided; if not, create a new compliance policy
let complianceid: string;
if (!req.body.complianceid) {
context.log('No complianceid provided, creating a new compliance policy');
const compliancePolicy = await compliancePolicies.postCompliancePolicy(accessToken);
complianceid = compliancePolicy.body.id;
context.log('Created compliance policy with id:', complianceid);
} else {
complianceid = req.body.complianceid;
context.log('Using provided complianceid:', complianceid);
}
// Assign the policy to the specified group
context.log('Assigning policy with complianceid:', complianceid, 'to groupId:', req.body.groupId);
const response = await compliancePolicies.assignPolicy(
complianceid,
req.body.groupId,
accessToken
);
// Prepare and send the HTTP response
context.res = {
status: 201,
body: response.body
};
context.log('Response sent');
} catch (error) {
context.log.error('Error processing request:', error.message);
context.res = {
status: 500,
body: { message: 'Internal Server Error' }
};
}
};
export default httpTrigger;
Detalhes Técnicos
Classe ServicePrincipal
Responsável pela autenticação com Azure AD utilizando ClientSecretCredential do pacote @azure/identity.
import { ClientSecretCredential } from "@azure/identity";
/**
* ServicePrincipal class to handle Azure AD authentication.
*/
export class ServicePrincipal {
/** The resource URL for Azure management. */
private readonly resource: string = "https://management.azure.com/.default";
/**
* Creates an instance of ServicePrincipal.
*
* @param {string} tenantId - The Azure AD tenant ID.
* @param {string} clientId - The client ID of the Azure AD app.
* @param {string} clientSecret - The client secret of the Azure AD app.
*/
constructor(
private readonly tenantId: string,
private readonly clientId: string,
private readonly clientSecret: string
) {}
/**
* Retrieves an access token from Azure AD.
*
* @returns {Promise<string>} - A promise that resolves to the access token.
* @throws {Error} - Throws an error if the access token cannot be acquired.
*/
public async getAccessToken(): Promise<string> {
try {
const credential = new ClientSecretCredential(this.tenantId, this.clientId, this.clientSecret);
const tokenResponse = await credential.getToken(this.resource);
if (!tokenResponse) {
throw new Error("Failed to acquire access token");
}
return tokenResponse.token;
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error acquiring access token:", error);
throw new Error("Failed to acquire access token");
}
}
}
Interface CompliancePolicy
Onde está declarado o tipo de dados a ser enviado a API do Graph API:
/**
* Represents a compliance policy.
*/
export interface CompliancePolicy {
/** The OData type of the policy. */
"@odata.type": string;
/** Indicates if an active firewall is required. */
activeFirewallRequired: boolean;
/** Indicates if anti-spyware is required. */
antiSpywareRequired: boolean;
/** Indicates if antivirus is required. */
antivirusRequired: boolean;
/** Indicates if BitLocker is enabled. */
bitLockerEnabled: boolean;
/** Indicates if code integrity is enabled. */
codeIntegrityEnabled: boolean;
/** Indicates if Windows Defender is enabled. */
defenderEnabled: boolean;
/** The description of the compliance policy. */
description: string;
/** Indicates if device threat protection is enabled. */
deviceThreatProtectionEnabled: boolean;
/** The required security level for device threat protection. */
deviceThreatProtectionRequiredSecurityLevel: string;
/** The display name of the compliance policy. */
displayName: string;
/** The required password type. */
passwordRequiredType: string;
/** The role scope tag IDs. */
roleScopeTagIds: string[];
/** Indicates if real-time protection is enabled. */
rtpEnabled: boolean;
/** The scheduled actions for the rule. */
scheduledActionsForRule: ScheduledActionForRule[];
/** Indicates if secure boot is enabled. */
secureBootEnabled: boolean;
/** Indicates if the signature is out of date. */
signatureOutOfDate: boolean;
/** Indicates if TPM is required. */
tpmRequired: boolean;
}
/**
* Represents a scheduled action for a rule.
*/
interface ScheduledActionForRule {
/** The name of the rule. */
ruleName: string;
/** The scheduled action configurations for the rule. */
scheduledActionConfigurations: ScheduledActionConfiguration[];
}
/**
* Represents a scheduled action configuration.
*/
interface ScheduledActionConfiguration {
/** The type of action. */
actionType: string;
/** The grace period in hours for the action. */
gracePeriodHours: number;
/** The list of email addresses to be CC'd in the notification message. */
notificationMessageCCList: string[];
/** The ID of the notification template. */
notificationTemplateId: string;
}
Classe CompliancePolicies
Encapsula lógica para criação e atribuição de políticas de conformidade utilizando Microsoft Graph API. Inclui métodos para postar novas políticas e atribuí-las a grupos.
import axios, { AxiosRequestConfig } from "axios";
import { CompliancePolicy } from "../interfaces/CompliancePolicy";
/**
* Interface extending CompliancePolicy to include additional properties.
*/
interface OutputCompliancePolicy extends CompliancePolicy {
id: string;
createdDateTime: Date;
lastModifiedDateTime: Date;
}
/**
* CompliancePolicies class to handle creating and assigning compliance policies.
*/
export class CompliancePolicies {
/** The base URL for Microsoft Graph API. */
private graphBaseUrl: string = "https://graph.microsoft.com/beta";
/**
* Creates an instance of CompliancePolicies.
*
* @param {string} name - The display name of the compliance policy.
* @param {string} description - The description of the compliance policy.
*/
constructor(private readonly name: string, private readonly description: string) {}
/**
* Creates a new compliance policy in Microsoft Graph.
*
* @param {string} accessToken - The access token for authentication.
* @returns {Promise<{status: number, body: OutputCompliancePolicy}>} - A promise that resolves to the created compliance policy.
* @throws {Error} - Throws an error if the HTTP request fails.
*/
async postCompliancePolicy(accessToken: string) {
try {
const url = `${this.graphBaseUrl}/deviceManagement/deviceCompliancePolicies`;
const policy: CompliancePolicy = {
"@odata.type": "#microsoft.graph.windows10CompliancePolicy",
activeFirewallRequired: true,
antiSpywareRequired: true,
antivirusRequired: true,
bitLockerEnabled: true,
codeIntegrityEnabled: true,
defenderEnabled: true,
description: this.description,
deviceThreatProtectionEnabled: false,
deviceThreatProtectionRequiredSecurityLevel: "unavailable",
displayName: this.name,
passwordRequiredType: "deviceDefault",
roleScopeTagIds: ["0"],
rtpEnabled: true,
scheduledActionsForRule: [
{
ruleName: "PasswordRequired",
scheduledActionConfigurations: [
{
actionType: "block",
gracePeriodHours: 12,
notificationMessageCCList: [],
notificationTemplateId: "",
},
{
actionType: "retire",
gracePeriodHours: 4320,
notificationMessageCCList: [],
notificationTemplateId: "",
},
],
},
],
secureBootEnabled: true,
signatureOutOfDate: true,
tpmRequired: true,
};
const config: AxiosRequestConfig = {
headers: {
Authorization: `Bearer ${accessToken}`,
"Content-Type": "application/json",
},
};
const response = await axios.post<OutputCompliancePolicy>(url, policy, config);
return {
status: 201,
body: response.data,
};
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error creating compliance policy:", error);
throw new Error("Failed to create compliance policy");
}
}
/**
* Assigns a compliance policy to a group in Microsoft Graph.
*
* @param {string} policyId - The ID of the compliance policy.
* @param {string} groupId - The ID of the group to assign the policy to.
* @param {string} accessToken - The access token for authentication.
* @returns {Promise<{status: number, body: any}>} - A promise that resolves to the response of the assignment operation.
* @throws {Error} - Throws an error if the HTTP request fails.
*/
public async assignPolicy(policyId: string, groupId: string, accessToken: string) {
try {
const url = `${this.graphBaseUrl}/deviceManagement/deviceCompliancePolicies/${policyId}/assign`;
const assignment = {
assignments: [
{
target: {
"@odata.type": "#microsoft.graph.groupAssignmentTarget",
groupId: groupId,
},
},
],
};
const config: AxiosRequestConfig = {
headers: {
Authorization: `Bearer ${accessToken}`,
"Content-Type": "application/json",
},
};
const response = await axios.post(url, assignment, config);
return {
status: 201,
body: response.data,
};
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error assigning compliance policy:", error);
throw new Error("Failed to assign compliance policy");
}
}
}
Conclusão
Automatizar a gestão de políticas de conformidade usando Azure Functions e TypeScript não apenas simplifica operações, mas também melhora a segurança e conformidade organizacional. Com essa implementação, empresas podem manter um ambiente seguro e compliance sem esforço adicional.
Referências
- Criar windows10CompliancePolicy – Microsoft Graph v1.0
- Automatizando a configuração de políticas de conformidade via Powershell com Microsoft Graph
- GitHub – sertaoseracloud/func_compliance_policies

